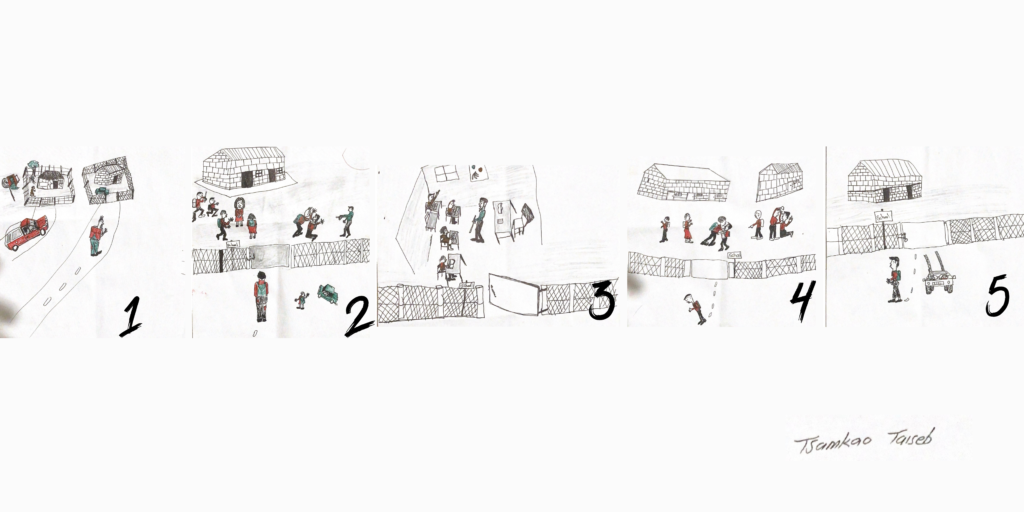

San Speaking elder went on a search to find KhoeKhoe Speaking teachers to teach the language at the school in his community.
USAID funds various programs in Namibia that support education and cultural preservation, including initiatives aimed at preserving indigenous languages and knowledge. These include the Ambassadors Fund for Cultural Preservation, which supports projects in the conservation of cultural objects, including archaeological and ethnographic items, as well as the restoration and preservation of historical buildings, sacred places, and monuments. Additionally, the PEPFAR Small Grants support the documentation and teaching of indigenous languages, as well as programs that incorporate traditional ecological knowledge to promote environmental conservation and education.
Established in 2008, the Ministry of ICT (MICT) oversees Information Technology, Telecommunication, and Broadcasting in Namibia. The ministry develops policies and legislation to advance the government’s digital agenda. MICT has established 25 Multi-purpose Community Centres in remote areas, equipped with internet infrastructure to enhance connectivity. Additionally, through the Namibia Film Commission’s outreach programs, Mobile Cinemas have been introduced to 199 villages and settlements, fostering a screen culture in rural communities. These initiatives showcase educational, informative, and entertaining films to keep communities informed about historical and current affairs in Namibia and beyond.
The National Institute for Educational Development (NIED), a directorate within Namibia’s Ministry of Education, Arts and Culture (MoEAC), has introduced various policies to support formal and non-formal education. These include the Environmental Education (EE) and Education for Sustainable Development (ESD) policies, as well as the Human Resource Development Plan. These initiatives aim to integrate Indigenous knowledge systems into the educational curriculum through community involvement, teacher training, capacity building, and the promotion of bilingual education.
UNESCO serves as the lead UN Agency for the implementation of the International Decade of Indigenous Languages (IDIL 2022-2032). UNESCO mobilizes stakeholders and resources for the preservation, revitalization and promotion of indigenous languages. UNESCO supports the development of national action plans.
The Indigenous Minorities Youth Organisation of Namibia (IMYON) was established during the National Conference for Youth from Marginalised Communities and Indigenous Minorities in May 2023. Ministry of Gender Equality, Poverty Eradication and Social Welfare. (2023) IMYON aims to empower marginalised youth, including the San, Ovatue, and Ovatjimba, through education and leadership development. The organisation conducts workshops and training sessions to equip youth with essential skills, advocates for their rights, and teaches them how to effectively represent their peers. Collaborating with the UN and the National Youth Council, IMYON enhances its capacity to support its initiatives. By providing a unified platform, IMYON amplifies the voices of marginalised youth, enabling them to participate in decision-making processes and work towards a more inclusive and prosperous society in Namibia.
The Endangered Languages Association of Namibia (ELAN) aims to preserve Namibian indigenous culture and identity through written discourse in indigenous or vernacular languages.
Palms for Life is an organization committed to uplifting minority communities in Namibia, particularly the San and Nama communities. Their efforts focus on alleviating poverty and promoting education, health, and cultural preservation. They have established 10 Early Childhood Development (ECD) centres, providing quality education to approximately 450 children annually in remote areas. They also offer vocational training to around 1,550 youths and adult literacy programs benefiting 53 individuals. Additionally, they have provided internet access to 6,800 people. To preserve cultural heritage, they produce educational materials, conduct training in Indigenous languages, and create an annual calendar celebrating San culture.
MGEPESW is committed to fostering an enabling environment and providing equal opportunities for sustainable socio-economic development and the well-being of targeted groups. The organization leads efforts to integrate Indigenous knowledge into national policies, ensuring that traditional practices and languages are recognized and preserved at the governmental level (Ministry of Gender Equality, Poverty Eradication and Social Welfare, 2020). This includes organizing various youth conferences with Indigenous communities. Additionally, MGEPESW’s mandate encompasses the preservation of Indigenous knowledge (IK) and Indigenous languages (IL) through its four pillars: Gender Equality and Related Human Rights Advocacy, Socio-Economic Development for Women, Girls, Boys, and Minority Communities, Stakeholder Coordination, and Institutional Excellence.
ygyufutufufufigufuffufygiyu


text
text
text
Text
extra text
extra text
Some extra text
