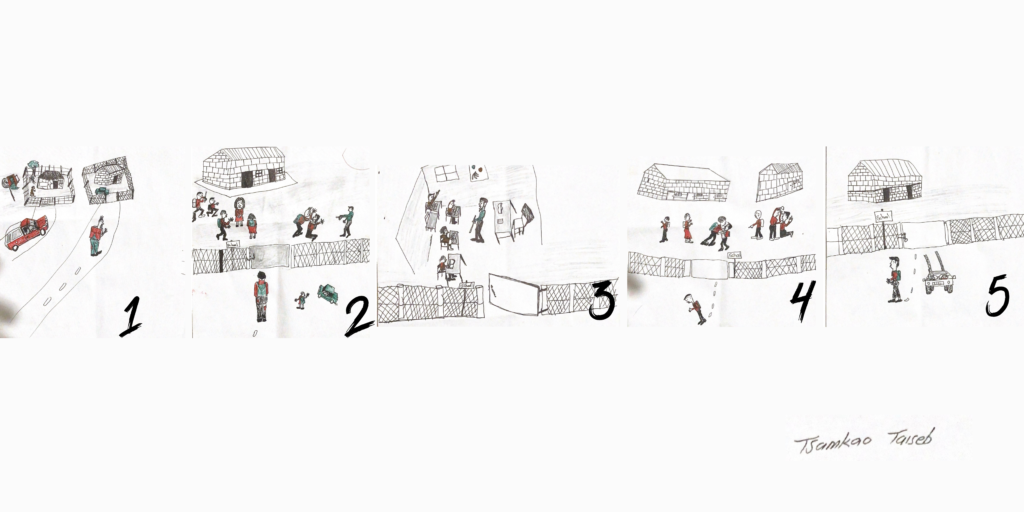
The ability to use indigenous languages and traditional practices directly affects the wellbeing of community members. Thus it is imperative that multilingualism and multi-culturalism are embraced to offer better health provision, recognizing traditional systems of medicine, as well as promoting social cohesion and delivering humanitarian responses, especially during health crises, and natural disasters.
Challenges






Strategies
Integrate indigenous knowledge into health care practices
Actions |
Actors |
|---|---|
| Integrate traditional healers into national health system | |
| Integrate traditional medicine and practices into national health system | |
| Train health workers in Indigenous knowledges (midwife, traditional birth practices, nutrition, healing) | |
| Create awareness amongst health care workers and patients on dual health system to facilitate integration and acceptance |
Ensure communication in indigenous language in health services
Actions |
Actors |
|---|---|
| Train health care workers in Indigenous languages | |
| Provide consultations in Indigenous languages (either provide translator or personnel speaks Indigenous languages) | |
| Translate medical forms and reports in Indigenous languages | |
| Translate health educational material in Indigenous languages | |
| Health campaigns in Indigenous languages |
Revive indigenous community-health practices
Actions |
Actors |
|---|---|
| Encourage community to use traditional health practices | |
| Create awareness on dual heath system | |
| Establish community health centres with resources (information, medicine, etc) |
Enhance mental health and well-being
Actions |
Actors |
|---|---|
| Integrate traditional practices into communal mental health services | |
| Translate mental health educational material in Indigenous languages | |
| Train mental health care workers in Indigenous languages | |
| Train mental health care workers in culturally sensitive mental health practices | |
| Programs to strengthen mental health and well-being through cultural empowerment | |
| Offer mental health services in Indigenous languages |
Initiatives
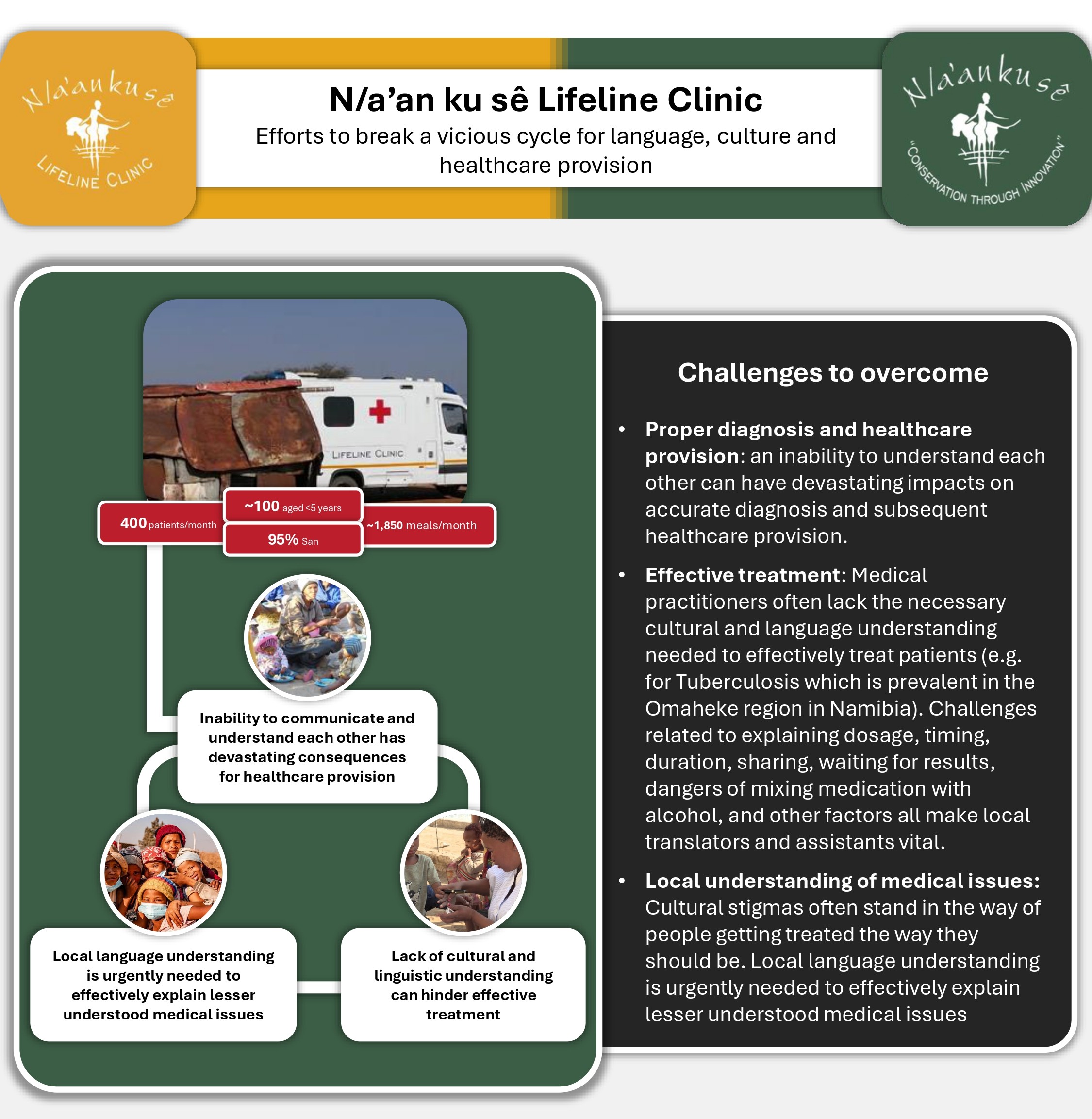
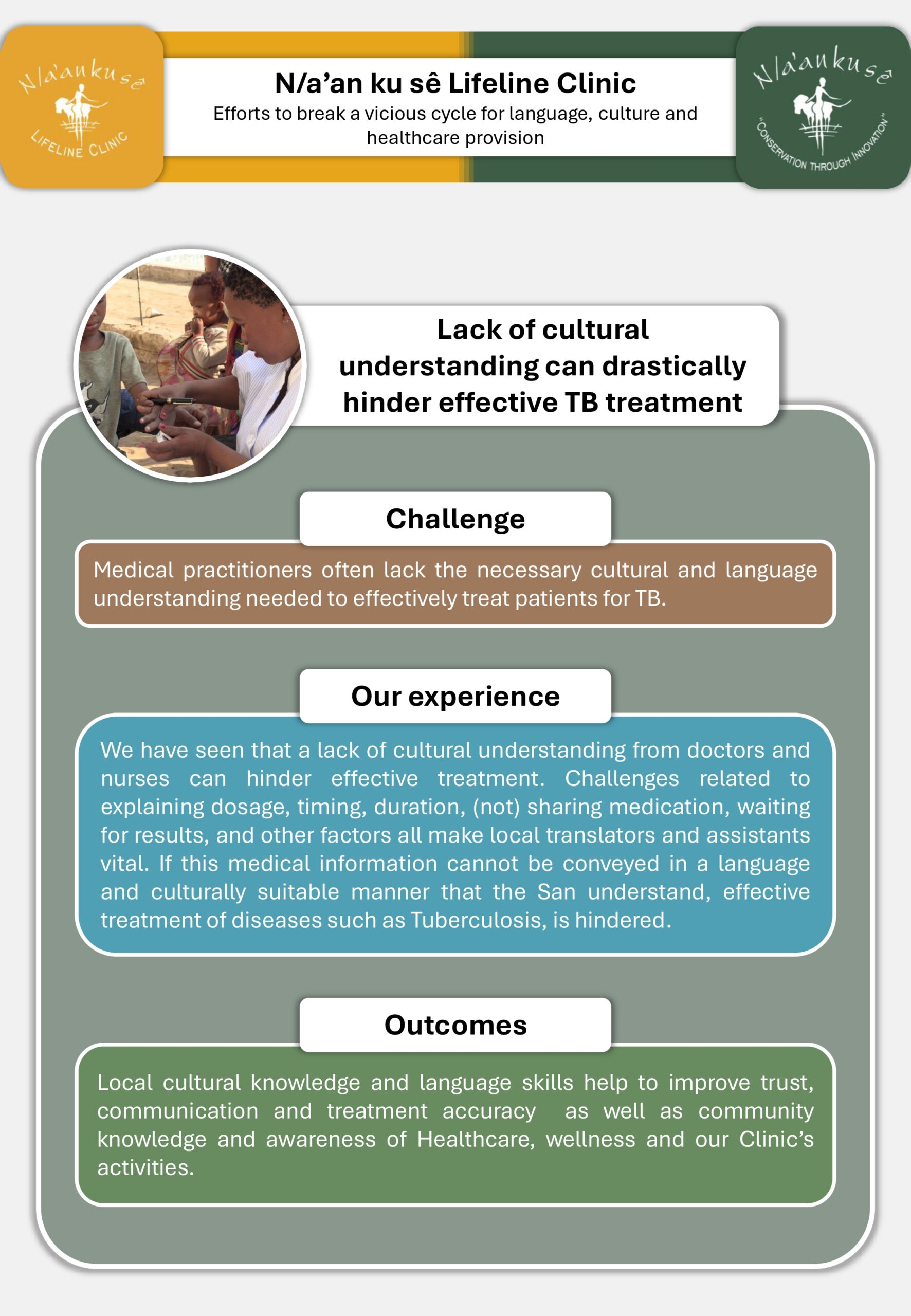
N/a’an ku sê Lifeline Clinic
Efforts to break a vicious cycle for language, culture and healthcare provision